After you have completed a full analysis from either FASTQ or VCF files as an input, you can perform further sub-analyses using the available Algorithmic filters. Below we demonstrate two example workflows:
- Select "Algorithmic filter analysis" from "Launch analysis" drop-down options.
- From the Analysis box drop-down choose the analysis you wish to apply the algorithmic filter to and on the right, choose from the available filters for your analysis. The icon links to information about the application of each filter.
"Trio Recessive (n= 3 )" filter example:
In this case,our analysis is a Family Trio and we filter for variants that are pathogenic that may be causative of recessive disorders in the child of unaffected parents.
We follow this selection process:
-
We exclude variants that are homozygous for the alternative allele in either parent.
-
We exclude variants in mitochondria and chromosome Y.
-
We keep variants where EITHER of these criteria apply:
-
Variant is homozygous for the alternative allele in the child.
-
Child is heterozygous and the following two criteria BOTH apply:
-
There are two or more variants in the same gene. To qualify, a variant must be in a coding transcript of a gene with a Transcript Support Level consistent with the sample’s settings. The variant must be Pathogenic, Likely Pathogenic or of Uncertain Significance (VUS).
-
The variants did not all come from the same parent; some variants on the gene may have come from the mother and some from the father or are de novo.
-
-
We want all VUS variants to be reported regardless of the triggered rules and their strength, so the "Strong VUS" option will not be selected. We also have the choice to keep only the variants that are missing from at least one parent by selecting the "Missing from one parent" option and we can exclude any variants that are found with a frequency greater than the selected threshold.
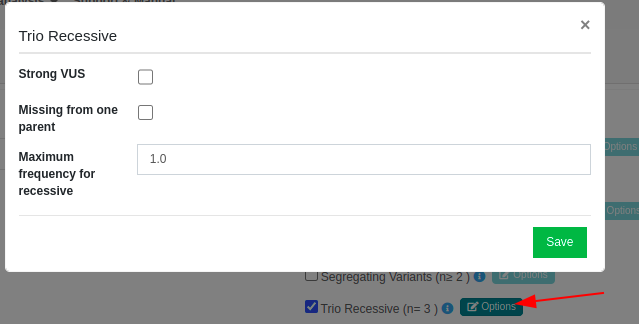
Once the parameters of the filter are set we click on the "Save" button and then on the  on the bottom of the page.
on the bottom of the page.
We recommend that you further filter by genes with recessive mode of inheritance or loss-of-function pathogenicity.
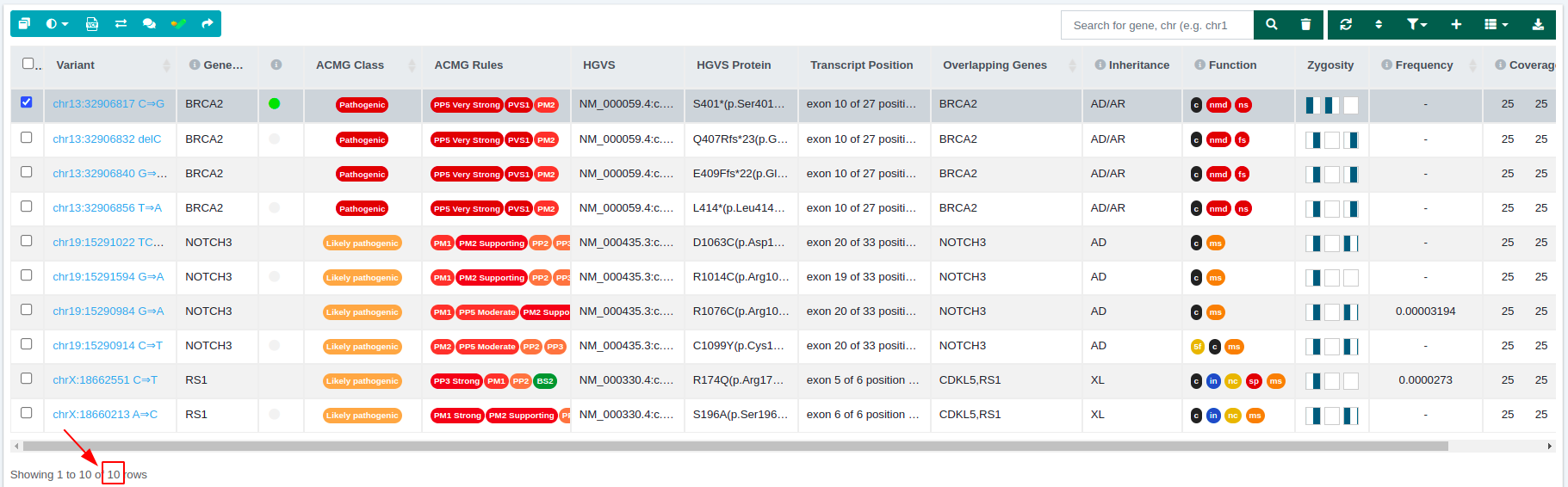
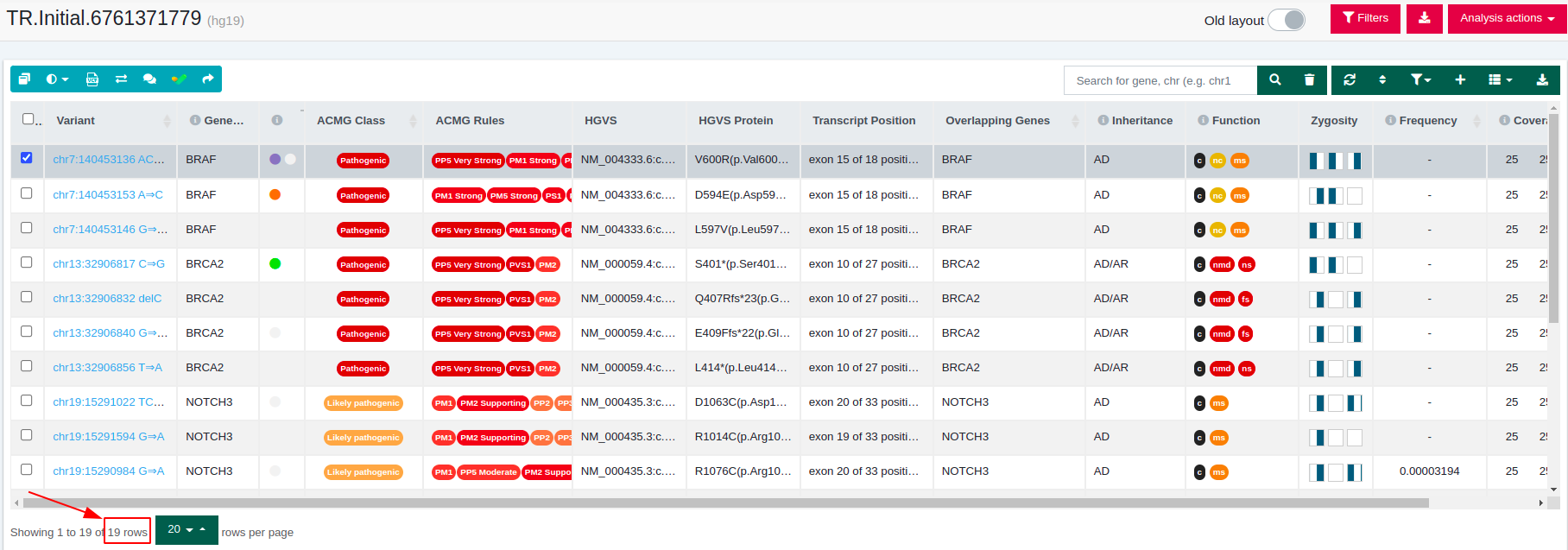
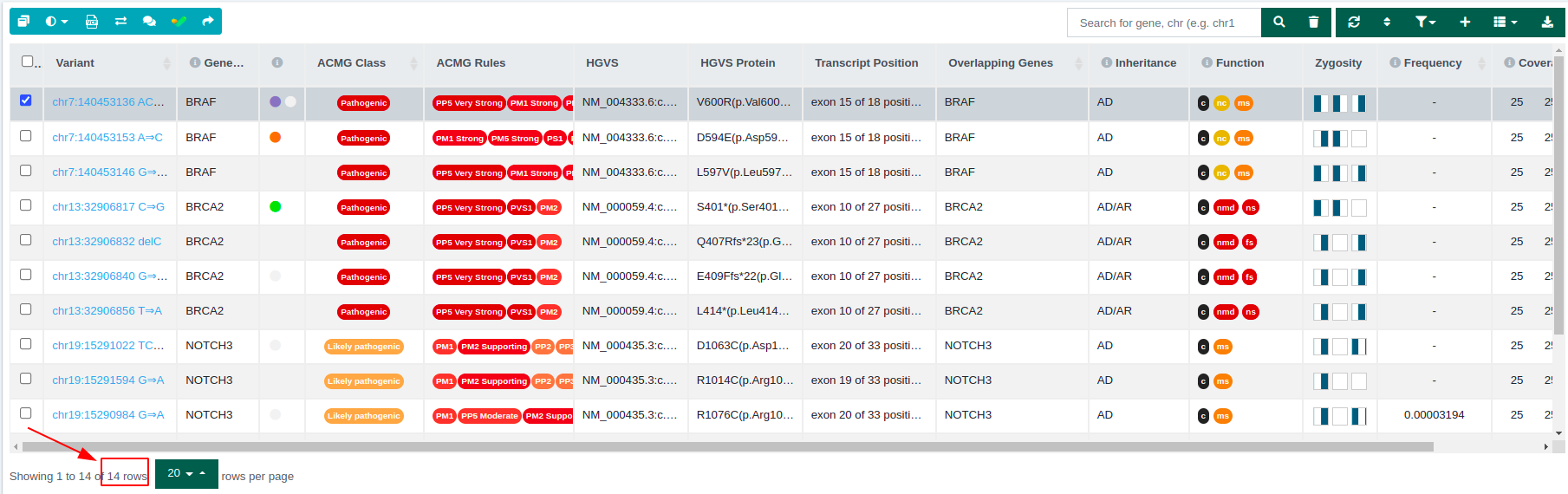
From 19 variants of the initial data set, we end up with 10 variants passing the filter.
- Initial analysis variant table:
- Sub analysis using the "Trio Recessive - All VUS" filter variant table:
We applied two more filters, a list with known cancer driver genes and a filter for Autosomal mode of inheritance (Dominant and Recessive) and and ended up with 15 candidate variants.
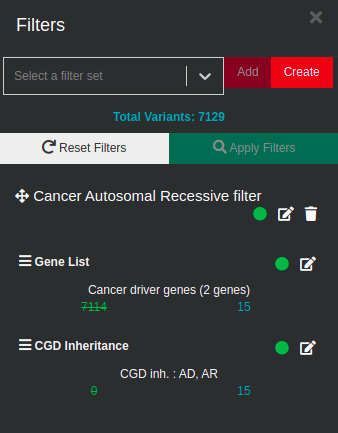
- Sub analysis using the "Trio Recessive - All VUS" filter sub sequentially filtered according to a list with known cancer driver genes and for Autosomal mode of inheritance (Dominant and Recessive) variant table: